Understanding What It Really Means to Crawl a Website
Crawling a website is fundamental to how search engines operate. Understanding this process is key to improving your site's visibility. Imagine a librarian meticulously cataloging every book in a vast library—that's essentially what a web crawler does. These automated bots, also known as spiders, systematically browse the internet, following links from page to page, just as you would click through a website. They collect data on each page, constructing an index that search engines use to deliver relevant search results.
This isn't a random process. Crawlers adhere to specific algorithms to determine which pages to visit and how frequently. They begin with a list of known URLs and then follow links on those pages to discover new ones. Think of it like exploring a city: you start at a central location and branch out, exploring various streets and neighborhoods.
How Crawlers Interpret Website Content
Crawlers don't "read" web pages as humans do. Instead, they analyze the underlying code, particularly the HTML, to understand the content and structure of each page. They focus on elements like title tags, meta descriptions, headings, and the text within the body of the page. This information helps search engines determine a page's topic and its relevance to specific search queries.
Modern crawlers are also becoming more adept at processing JavaScript. While JavaScript allows for more dynamic and interactive web experiences, it can also pose challenges for crawlers if not implemented correctly. Ensuring your JavaScript renders correctly for bots is essential for accurate indexing of your content. This increasing complexity emphasizes the importance of understanding how crawlers function.
The scale of this operation is immense. For perspective, Google, the most popular website globally, receives roughly 175 billion visits monthly from approximately 9.01 billion unique users. The average internet user visits around 130 web pages daily, totaling roughly 4,000 pages monthly. With 93% of online experiences originating from a search engine, crawlers like Googlebot are constantly indexing and updating content. This ensures search results are both relevant and current. Find more detailed statistics here: Learn more about website statistics. This continuous activity demonstrates the crucial role crawlers play in connecting users with the information they need. Optimizing your website for these crawlers is therefore essential for online success.
Different Types of Crawlers and What They Mean for You
Understanding the different types of web crawlers is essential for effective website optimization. These automated bots, with their distinct purposes and behaviors, interact with your site in various ways, impacting your overall strategy.
Search Engine Crawlers
The most common crawlers are those used by search engines like Google (Googlebot), Bing (Bingbot), and Yandex (YandexBot). These crawlers index web pages to populate search results. Their main goal is to understand your website's content and structure, determining its relevance to user searches. Optimizing your website for these crawlers is crucial for high search engine rankings.
Social Media Crawlers
Social media platforms also utilize crawlers. Bots like Facebook's crawler and Twitter's bot extract information from shared links to create preview snippets within posts. These crawlers look for specific meta tags, such as Open Graph and Twitter Cards, to display engaging images, titles, and descriptions.
Other Specialized Crawlers
A wide array of specialized crawlers exists beyond search engines and social media. These include research crawlers used by academic institutions, monitoring bots that track website performance, and crawlers used by marketing analytics tools. This diverse ecosystem of automated agents collects data for various purposes, from search indexing and social media sharing to market analysis. For example, Baidu dominates the search market in China with approximately 195.7 million visits per month, significantly influencing which sites its crawler prioritizes. Learn more about the variety of web crawlers: Explore this topic further.
To further illustrate the different types of crawlers, their parent companies, primary purposes, geographic focus, and crawl frequency, let's look at the table below.
Major Web Crawlers by Platform and Purpose
| Crawler Name | Parent Company | Primary Purpose | Geographic Focus | Crawl Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Googlebot | Search indexing | Global | High | |
| Bingbot | Microsoft | Search indexing | Global | Medium |
| YandexBot | Yandex | Search indexing | Russia and surrounding countries | Medium |
| Facebook crawler | Meta | Social media link previews | Global | Medium |
| Twitter bot | Social media link previews | Global | Medium | |
| Baidu Spider | Baidu | Search indexing | China | High |
| Various | Academic Institutions | Research and data collection | Varies | Low to Medium |
| Various | Monitoring Services | Website performance tracking | Varies | Varies |
The table above highlights some of the most influential web crawlers and their specific functions across different online platforms and regions. Understanding their respective roles can be beneficial for tailoring your website optimization strategy.
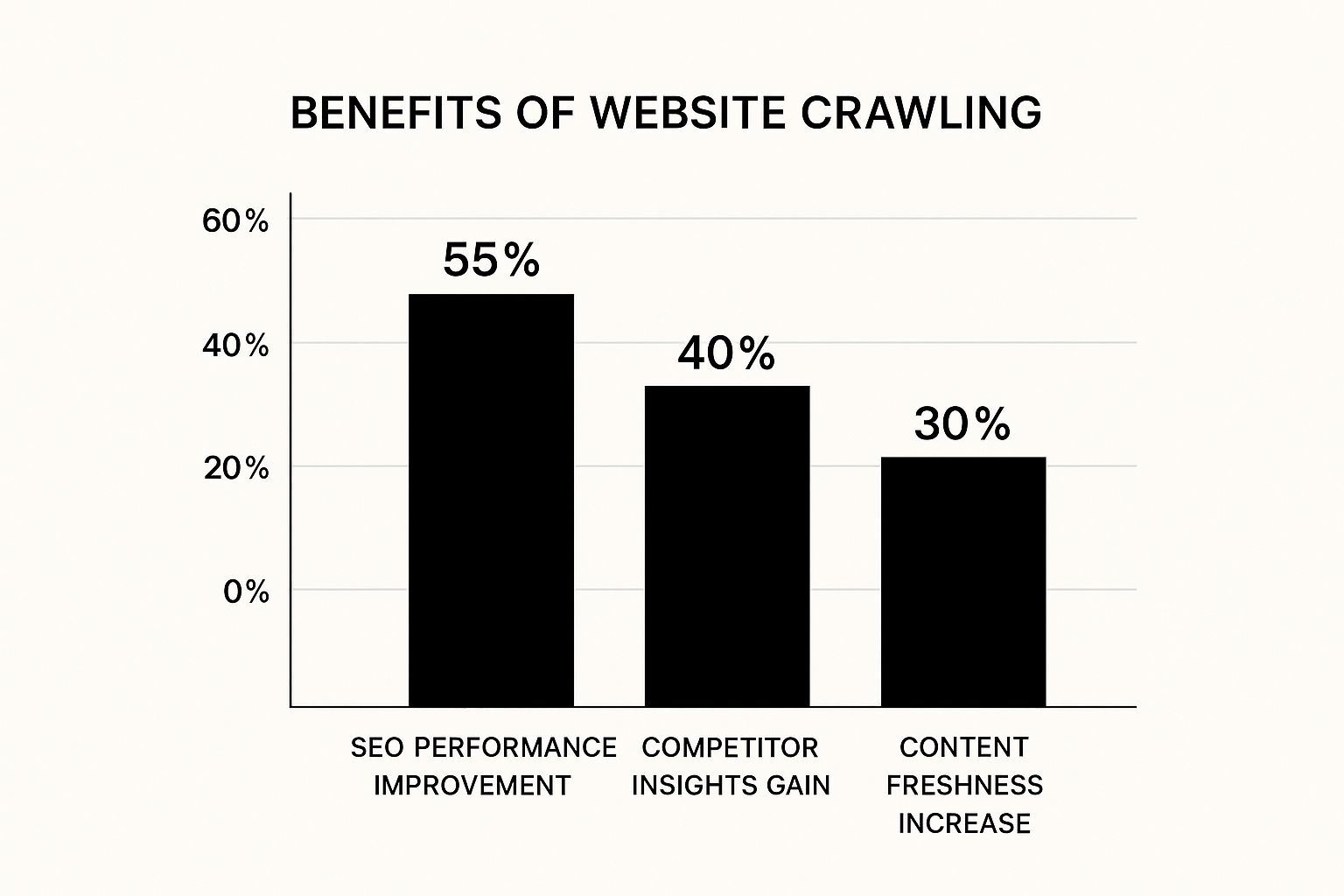
The infographic above visualizes the key benefits of understanding web crawling. Optimizing for these crawlers can significantly improve SEO performance, provide valuable competitor insights, and maintain content freshness. These improvements demonstrate the importance of understanding crawler functionality for a successful online strategy.
Essential Tools and Methods That Actually Work
Ready to crawl a website effectively? This section explores the essential tools and techniques SEO professionals use, from free options to enterprise-level platforms. We'll discuss setting up crawls, handling JavaScript, and approaching password-protected areas.
Choosing the Right Crawling Tool
Choosing the right crawling tool depends on your website's size, budget, and the data you need. A smaller website (under 500 URLs) might find Screaming Frog’s free version sufficient. Larger sites or more complex analyses may require a paid version or a different platform.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: A popular choice, Screaming Frog offers both free and paid versions, providing data on website structure, broken links, redirects, and more.
- Semrush Site Audit: Part of the Semrush suite, this tool provides a complete site audit, including crawlability assessments, technical SEO issue identification, and actionable recommendations.
- Ahrefs Site Audit: Similar to Semrush, Ahrefs offers a powerful site audit tool uncovering crawling issues, broken links, and other technical SEO problems impacting website performance.
- DeepCrawl: A cloud-based crawler, DeepCrawl excels with larger websites and enterprise-level needs, offering detailed log file analysis and advanced reporting.
Setting Up and Executing Your Crawl
After choosing your tool, setting up the crawl correctly is crucial. This involves specifying the website URL, setting the crawl depth (how many links deep the crawler should follow), and configuring parameters like crawl rate to avoid overloading the server.
- Respect Robots.txt: Crawlers should respect the
robots.txtfile, which guides bots on which website sections to avoid. This is crucial for ethical crawling. - Set Crawl Delays: Adjusting crawl delay prevents server overload, ensuring a smooth crawl. This also maintains a good relationship with website owners.
- Handle JavaScript: Many websites use JavaScript, and not all crawlers handle it well. If your target website relies heavily on JavaScript, use a tool like Screaming Frog with robust JavaScript rendering. This ensures the crawler sees the fully rendered page.
For example, if content loads dynamically with JavaScript after the initial page load, a crawler without proper JavaScript rendering might miss this content. Choosing a tool that processes JavaScript is essential for crawling modern websites.
Crawling Tricky Websites: JavaScript and Passwords
Crawling websites with dynamic content or password-protected areas presents unique challenges. For JavaScript-heavy sites, ensure your crawler renders JavaScript correctly. This might require specific tools or configurations.

Password-protected areas often require providing login credentials securely and ethically, respecting the website's terms of service. Consider using specific API integrations if available for a more controlled crawl. This process, while technical, is essential for accurate data. Like exploring a complex maze, website crawling requires the right tools and knowledge to navigate effectively. By following these tips and choosing the right methods, you can crawl a website efficiently and gain valuable SEO insights.
Making Your Website Crawler-Friendly (The Smart Way)
Optimizing your website for crawlers goes beyond simply adhering to best practices. It involves understanding how search engines perceive and interact with your content. This understanding allows you to structure your website for efficient content discovery and indexing, leading to improved search engine rankings and faster data processing.
Crawl Budget: Speed Over Size
A crucial aspect of website management is understanding crawl budget. This refers to the number of pages Googlebot will crawl on your website within a given timeframe. Having a large number of pages doesn't guarantee more frequent or deeper crawls. Even sites with up to 1 million pages aren't solely evaluated based on size.
According to Google's Search Relations expert Gary Illyes, website speed and server performance are the primary factors influencing crawl depth and frequency. This means a fast, well-optimized website with fewer pages might be crawled more thoroughly than a larger, slower site. For more information on this topic, you can Discover more insights about crawl budget.
Optimizing Server Performance and Internal Linking
Imagine two libraries: one massive but disorganized, and another smaller but well-cataloged. The smaller, organized library allows faster information retrieval. Similarly, optimizing server response time and improving site architecture significantly impacts crawler access.
A robust internal linking strategy guides crawlers through your website, ensuring discovery of all important pages. Internal links act as pathways, connecting different sections and improving navigation. For further reading on crawlability, check out this article: How to master website crawlability.
Leveraging XML Sitemaps and Robots.txt
XML sitemaps provide crawlers with a comprehensive list of your pages, acting as a blueprint for your website. This helps crawlers find content, especially within complex website structures. This is particularly beneficial for larger websites.
While accessibility is key, controlling crawler access is equally important. The robots.txt file specifies directories or pages crawlers should ignore. This is helpful for excluding pages under development, private content, or duplicates, thereby optimizing your crawl budget. Best budget PA systems are featured in this article if you're working on crawling projects. Strategically using these tools ensures crawlers prioritize relevant content.
Advanced Techniques for Complex Crawling Challenges
Crawling a website can be more complex than simply deploying a basic crawler. Several challenges can arise, particularly with modern websites employing advanced technologies and security measures. This section explores these challenges and offers advanced solutions.
Handling JavaScript-Heavy Websites
Many websites rely heavily on JavaScript to load dynamic content. This can be problematic for basic crawlers, which might not fully render the JavaScript code, leading to incomplete data retrieval. The solution? Headless browsers.
A headless browser operates like a regular browser but without a graphical user interface. This allows it to render JavaScript and fully load dynamic content, providing the crawler with a complete picture of the page. This ensures that all data, even dynamically loaded content, is captured.
Navigating Dynamic Content and Anti-Bot Measures
Dynamic content, while enriching the user experience, often loads after the initial page load. Crawlers need to handle this delayed rendering to gather all necessary data. Furthermore, many websites employ anti-bot measures to prevent abuse. These measures can include rate limiting, CAPTCHAs, and IP blocking.
To overcome these hurdles, consider the following:
- Implement Proper Delays: Inserting delays between crawl requests mimics human behavior and reduces the likelihood of triggering anti-bot mechanisms. This practice is known as a politeness policy.
- Manage Session Authentication: Some websites require logins. Crawlers need to handle session authentication correctly to access restricted content. This might involve managing cookies and session IDs.
- Leverage APIs: When direct crawling is difficult or prohibited, using website APIs can offer a structured and efficient way to retrieve data. APIs are often designed for automated data access, offering a cleaner and more reliable solution. For further insights into competitor analysis, consider this resource: How to master SEO competitor analysis.
Building Custom Crawling Solutions
When off-the-shelf crawling tools prove inadequate, building a custom crawler using programming frameworks like Python provides greater control and flexibility. This approach allows you to tailor the crawler to specific needs, such as handling complex authentication flows or extracting specific data points.
However, building a custom solution demands more technical expertise and resources. It offers a powerful alternative for complex crawling scenarios.
Overcoming Crawl Blocking and Rate Limiting
Some websites actively try to block crawlers. They might implement IP blocking or rate limiting to restrict access. Respecting the instructions within the robots.txt file is critical. Rotating IP addresses can help avoid IP blocks.
To ensure your site remains easily crawlable, follow a thorough quality assurance process, as outlined in this Website QA Checklist. Careful monitoring and adaptation are crucial when encountering these challenges.

Crawling Behind Login Walls
Accessing content behind login walls presents a unique set of challenges. It requires secure handling of user credentials and careful adherence to the website's terms of service. Some crawlers offer features to manage login credentials, but this should always be done responsibly and ethically.
The following table summarizes common crawling challenges and their solutions.
Crawling Challenges and Solutions: Common website crawling obstacles and proven methods to overcome them
| Challenge | Impact Level | Recommended Solution | Tools Required | Implementation Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JavaScript-Heavy Websites | High | Headless Browser | Headless browser libraries (e.g., Puppeteer, Selenium) | Medium |
| Dynamic Content | Medium | Implement delays, use AJAX handling | Crawler with dynamic content support | Medium |
| Anti-Bot Measures | High | Politeness policy, IP rotation, CAPTCHA solving | Proxies, CAPTCHA solving services | High |
| Crawl Blocking | High | Respect robots.txt, use proper user agents | Crawler configuration, user agent management tools | Medium |
| Rate Limiting | Medium | Implement delays, adjust crawl rate | Crawler configuration | Easy |
| Content Behind Login Walls | High | Session management, credential handling | Crawler with login support, secure credential storage | High |
This table outlines common website crawling obstacles and effective strategies to navigate them, highlighting the complexity and required resources for each solution.
This section has covered several advanced techniques to address complex crawling challenges. Mastering these strategies will enable you to effectively crawl websites and gather the information you need.
Turning Crawl Data Into Actionable Insights

Collecting crawl data is just the first step. The real power lies in understanding how to analyze this data and turn it into actionable insights. This means identifying SEO opportunities, pinpointing technical issues, and prioritizing fixes for maximum impact. This process, much like planning the best route on a map, requires careful interpretation and a strategic approach.
Interpreting Crawl Reports and Spotting Patterns
Crawl reports offer a wealth of information, but it's easy to get bogged down in the details. Start by focusing on key metrics like broken links, slow loading times, and crawl errors. These issues directly impact user experience and search engine rankings.
Look for patterns in your data. For example, numerous 404 errors in a specific directory could indicate a structural problem with your website. Similarly, a consistent pattern of slow loading times might point to server issues.
Recognizing these patterns helps uncover larger, underlying problems. This allows you to address the root cause of the issue rather than just treating the symptoms. You might be interested in How to master SEO performance metrics for a deeper dive into this topic.
Setting Up Monitoring and Alert Systems
Once you've identified potential problems, setting up monitoring systems becomes crucial. These systems continuously crawl your website, tracking key metrics and alerting you to any significant changes.
This proactive approach lets you address issues before they negatively affect your search rankings or user experience. Think of it as an early warning system, notifying you of potential problems before they escalate into larger concerns.
Translating Technical Data Into Business Insights
Finally, it’s important to translate technical crawl data into business insights that stakeholders can understand. This means explaining the impact of technical issues on business goals, such as website traffic and conversions.
For example, you might show how fixing broken links can improve user engagement and lead to higher conversion rates. Clearly demonstrating the connection between technical SEO and business outcomes justifies the investment in optimization efforts.
This translation, similar to converting a complex formula into a simple graph, makes the data accessible and impactful. This clear communication bridges the gap between technical details and business outcomes. By understanding the impact of these issues, stakeholders can make informed decisions and prioritize necessary improvements.
Key Takeaways
Crawling a website isn't just a technical process; it's fundamental to online visibility and a cornerstone of any successful SEO strategy. This section highlights key takeaways from this guide, offering actionable steps you can implement right away, no matter your experience level.
Prioritize Website Speed and Performance
Website speed dramatically affects how search engines crawl your site. A fast-loading website, even with fewer pages, can outperform a larger, slower site in crawl depth and frequency. Focus on optimizing server response times, minimizing HTTP requests, and compressing images. This maximizes your crawl budget, ensuring search engines efficiently access and index your content.
Master Technical SEO Elements
Effective use of robots.txt and XML sitemaps is essential for technical SEO. Use robots.txt to guide crawlers, specifying which areas to avoid. Utilize XML sitemaps to provide a clear structure of your site. These tools ensure crawlers find and prioritize your most important content while respecting your site's boundaries.
Choose the Right Crawling Tools
Selecting appropriate crawling tools is crucial for efficient data collection. Screaming Frog is excellent for smaller websites, while enterprise-level solutions like DeepCrawl cater to larger, more complex sites. Consider your budget, website size, and data needs when making your choice. The right tool ensures efficient navigation and data retrieval.
Address JavaScript and Dynamic Content
Modern websites often use JavaScript for dynamic content, posing challenges for crawlers. Employ tools with strong JavaScript rendering capabilities to ensure all content is captured. Addressing JavaScript effectively ensures complete content indexing.
Handle Complex Crawling Challenges
For password-protected areas and websites with strict anti-bot measures, advanced techniques are necessary. Utilize headless browsers for complete content rendering, implement polite crawling practices, and consider using APIs where available. These techniques allow you to navigate even the most complex website structures.
Analyze Crawl Data for Actionable Insights
Data collection is just the first step. Analyze crawl reports to identify technical SEO issues like broken links, slow load times, and crawl errors. Prioritize fixes based on their impact on website performance and user experience. Analyzing data reveals opportunities for improvement and optimization.
Ready to improve your SEO? That's Rank offers a suite of tools to help you track keyword rankings, monitor SERP positions, audit website health, and compare competitor performance. Start optimizing your website today!